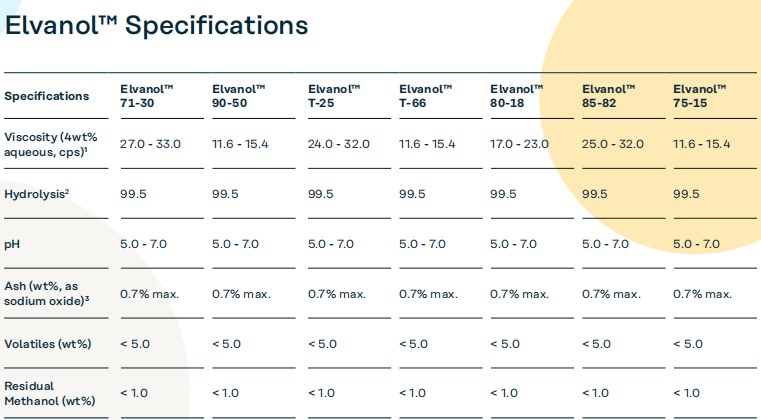
Since cleanroom facilities are designed with different levels of requirements depending on their usage, and some work environments require even higher cleanliness standards, FFU(Fan Filter Units) have thus been introduced. The emergence of FFU(Fan Filter Units) has effectively addressed this issue.Using FFU(Fan Filter Units) can effectively solve the problems present in cleanroom projects. The main points are as follows:
1.Space saving — Using FFU(Fan Filter Units)can save space and address the issue of limited maintenance space above the cleanroom ceiling.
High-standard cleanrooms often require Class 100 or even Class 10 laminar hoods to meet process requirements. In such cases, large supply air plenum boxes are installed above the cleanroom ceiling, with fans inside. These plenum boxes, along with supply and return air ducts, occupy significant space, reducing maintenance access and sometimes even affecting the use of fire escape routes.
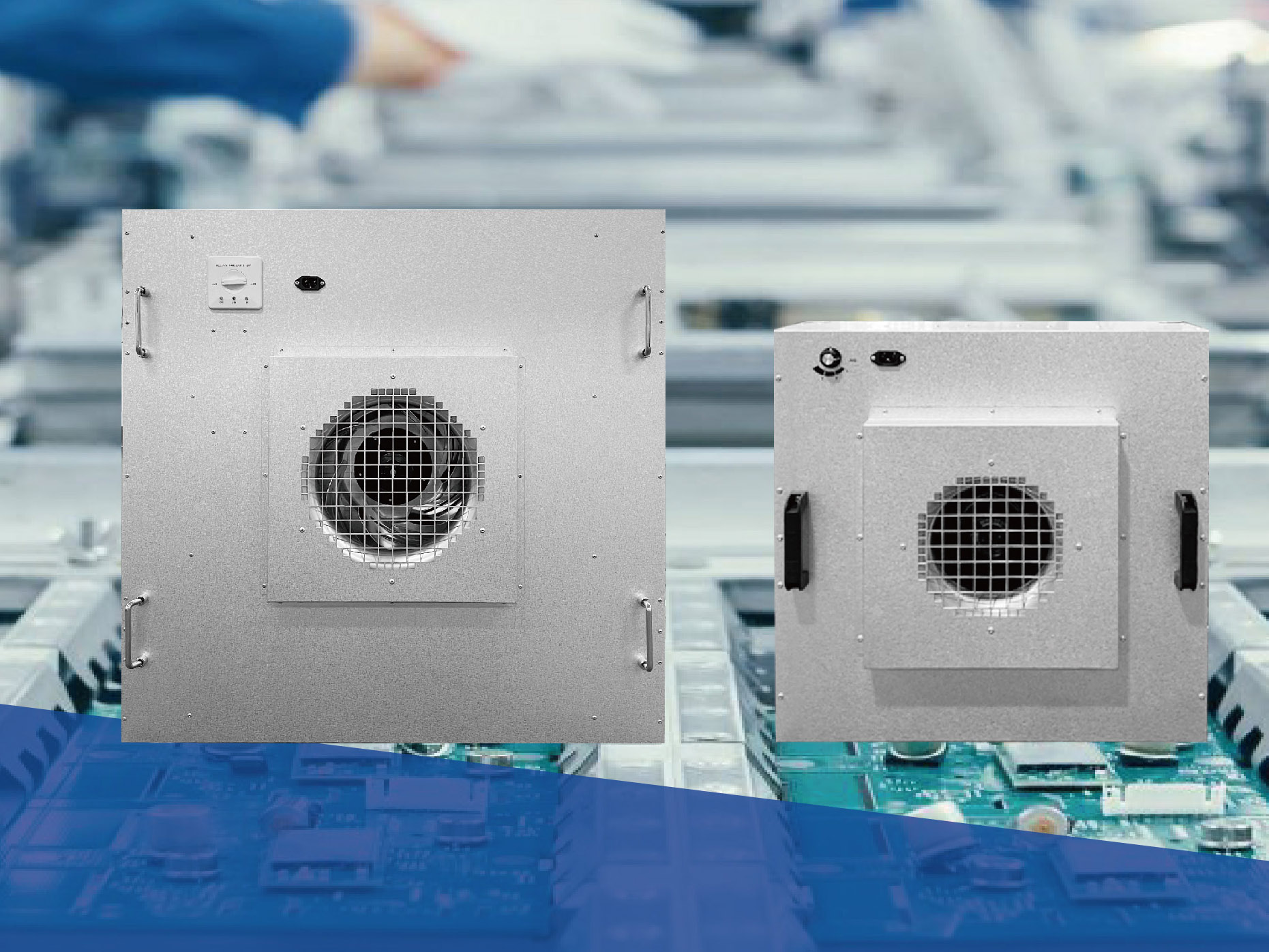

When FFUs are used, the cleanroom ceiling can be divided into multiple modules, with each module being an FFU. By adjusting each module, the pressure balance requirements of the supply air plenum above the ceiling can be met, significantly reducing the height requirements of the plenum. Additionally, the need for large supply and return ducts can be eliminated, saving installation space. FFUs are particularly effective in renovation projects where ceiling height is limited. Moreover, FFUs come in various sizes and can be customized according to the actual dimensions of the cleanroom. Because of this, they occupy less vertical space within the supply air plenum, and essentially do not occupy space within the cleanroom itself, thereby further maximizing space savings.
2. FFU Flexibility—By utilizing the structural features of the FFU's independence, adjustments can be made at any time, compensating for the limited maneuverability of the cleanroom and thereby addressing the disadvantage of production processes that are not easily adjustable.
The maintenance structure of cleanroom facilities is generally made of metal panels, and once constructed, the layout cannot be freely altered. However, due to continuous updates in production processes, the original cleanroom layout may no longer meet the requirements of new processes, leading to frequent modifications in the cleanroom for product upgrades, which results in significant financial and material waste.
By adjusting the number of FFUs, the cleanroom layout can be locally modified to accommodate process changes. Moreover, FFUs come with built-in power, air outlets, and lighting, which can save a substantial amount of investment. Achieving the same effect is nearly impossible for conventional integrated air supply purification systems.
Because FFUs are self-powered, they are not limited by specific areas. In a large cleanroom, zoning control can be implemented as needed. Additionally, as semiconductor production processes evolve, the facility layout inevitably requires corresponding adjustments. The flexibility of FFUs makes such adjustments easy without necessitating additional investment.
3. Reducing Operational Burden — The FFU system is energy-saving, thereby addressing the drawbacks of central air supply, such as large air conditioning rooms and increased operating costs of air handling units.
If individual cleanrooms within a large-area cleanroom facility require a higher level of cleanliness, the air volume of a centrally supplied air conditioning unit must be large and the fan pressure high to overcome the resistance of ducts as well as the resistance of primary, medium, and high-efficiency filters, in order to meet the requirements. Moreover, in a central air supply system, any failure of an air conditioning unit will cause all cleanrooms associated with that unit to cease operation.
Although the initial investment for using FFUs is higher than that for ducted ventilation, the system demonstrates outstanding energy-saving and maintenance-free characteristics during later operation, making FFUs more popular.